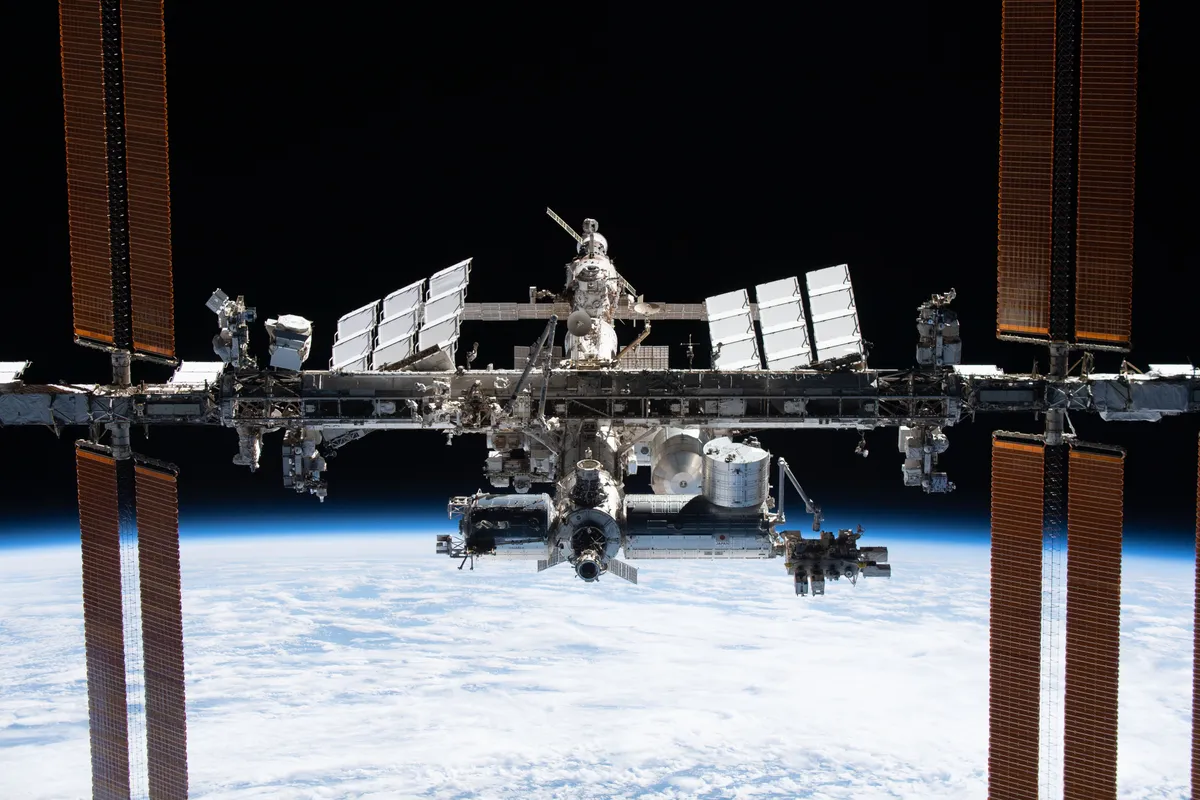
The International Space Station (ISS) will cease operation in January 2031. After that, NASA will remove the laboratory from Earth orbit so that it can fieryly reenter the atmosphere and crash into a remote region of the Pacific Ocean. Since its launch in November 2000, this probe has ensured the permanent survival of humans in space, but after the end, will there still be anyone in space?
For those in a hurry:
- The International Space Station has a set end date, but continued human survival in space is guaranteed;
- China’s Tiangong space station has been operational since 2021 and is expected to remain in orbit for a few more years;
- In addition, there are also other orbital laboratories that will be launched soon, such as the Axiom Station and the Russian Orbital Service Station (ROSS).
- The Moon will also get a representative in the coming years, the Gateway Space Station.
Tiangong Space Station
Well, the International Space Station is not the only space station in Earth’s orbit. In addition, there is the Chinese Tiangong Space Station. Construction began in April 2021 and currently consists of three units. In the future, the laboratory is expected to receive three more units and double its size.
The Tiangong space station is expected to last about 10 years, but with the addition of new modules, it may last a little longer. This means that even after the end of the International Space Station, China will be able to continue continuous human survival in space.
Read more:
Orbital laboratories that will be launched in the coming years.
In addition to Tiangong, private companies are also planning to launch their own space stations, which is one of them Axiom station. In the coming years, Axiom Space will launch modules that will be connected to the International Space Station for commercial space activities. When the International Space Station stops working, it will separate and orbit Earth alone.
The first module of the Axiom station will be launched in 2025, and by 2031, when it will orbit on its own, it will consist of six modules. The station will be able to accommodate up to 8 crew members, and will perform various functions such as laboratory, manufacturing facilities and recording studios. In a way, this will be a continuation of the ISS’s legacy of continued human survival in space.
Another space platform planned for the coming years is the one built by Russia. Construction of the Russian Orbital Service Station (ROS) will begin in 2027, with the launch of the NEM-1 module, which will initially be docked to the International Space Station.
In 2028, a second module will be launched, which is also the year Russia will leave the International Space Station. The ROSS building is scheduled to be completed in 2035 and will consist of 7 units. However, it is not known to what extent these plans have become a reality.
Now, we’re talking about another major international collaboration for human survival in space, the Gateway Space Station, which will orbit the Moon and be supported by NASA, the European Space Agency, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). ). The laboratory will serve as a gateway to the Moon and perhaps even Mars, and construction is expected to begin at the end of the decade.

“Hardcore beer fanatic. Falls down a lot. Professional coffee fan. Music ninja.”





More Stories
The law allows children and adolescents to visit parents in the hospital.
Scientists pave the way for the emergence of a new element in the periodic table | World and Science
Can dengue cause hair loss? Expert explains how the disease affects hair