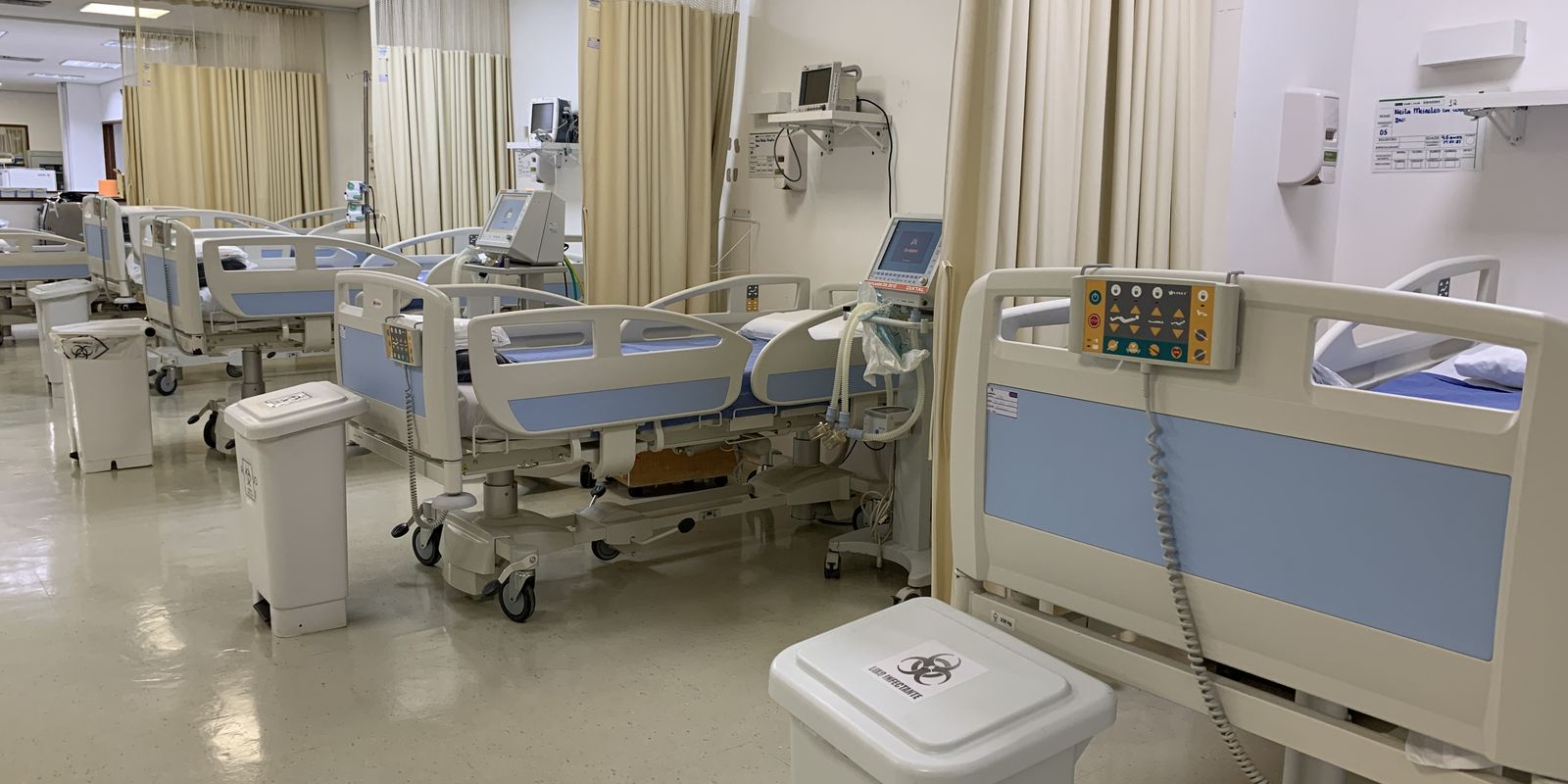
the stf I decided, in cases of long hospital stays and premature births, to start maternity leave It is considered After discharge from the hospital from the mother or the newborn. Understand the changes and new rights.
How was it before?
- The Legal Legal Obligation Act (CLT) defines the absence of pregnant women between the 28th day before delivery and the date the baby is born.
- Maternity leave is 120 days.
- Women are entitled to maternity benefits, which must be borne by Social Security.
- If there are any complications, the license is expected to be extended for two weeks upon presentation of a medical certificate.
What has changed?
- There has been a reinterpretation of the start of the furlough period, says lawyer Eloisa Burguelot.
- According to her, the main premise of social rights has not been fulfilled previously, that is, the observance of the right of women and children.
- Minister Edson Fashin decided the procedure, considering that starting the license inventory after demobilization is the right of the newborn, not just the mother.
- He said the current legislation does not take into account long hospitalizations, such as premature deliveries, before the 37th week of pregnancy.
Is the decision really correct?
- Going forward, the understanding will apply to long hospitalizations, greater than two weeks, and premature deliveries.
- The effect of the decision is immediate for all pregnant women and mothers who are employed in the formal labor system, which is governed by the Labor Code Act.
What if the president refuses?
- Economist Bruna Fortunato says that failure to comply with the law can result in legal penalties for the employer.
- The employer will only bear the cost of this if it chooses to hire a temporary person.
- In case Pregnancy Risk, the duty of the company is to pay the pregnant woman for the duration of the certificate.
- Then it falls to the National Institute of Social Security, with temporary disability assistance.
Can it affect the employment of women?
- The economist says the decision is a breakthrough.
- However, it does not exclude negative effects on the employment of women, as it may represent a longer period of absence from work.
What do you do in cases of dismissal?
- Eloísa explains that, by law, no woman can be separated while pregnant.
- If she is fired and it is later discovered that she is indeed pregnant, the employer must integrate her into the team again.
Unfortunately, the most common layoffs are after women return from vacation. At that time, what you can do is go to court.
Eloisa Bourguelot

“Hardcore beer fanatic. Falls down a lot. Professional coffee fan. Music ninja.”





More Stories
Sabesp Receives Brazil Innovation Value Award 2024 • PortalR3
Total formal job creation reached 201.7 thousand in June, up 29.6% | Economy
10,000 Brazilian Reals are waiting for you at Nubank? Find out who can get this money!