Over the years of life on planet Earth, many types of animals and plants have existed and today they are no longer part of our daily life. Several centuries ago, researchers described some fruits, for example, and they became extinct over the years. In this context, we list some Extinct foods throughout history.
Read more: What foods are already extinct and the reasons that led to their disappearance?
Discover some of the foods that have become extinct throughout history
1. The dodo
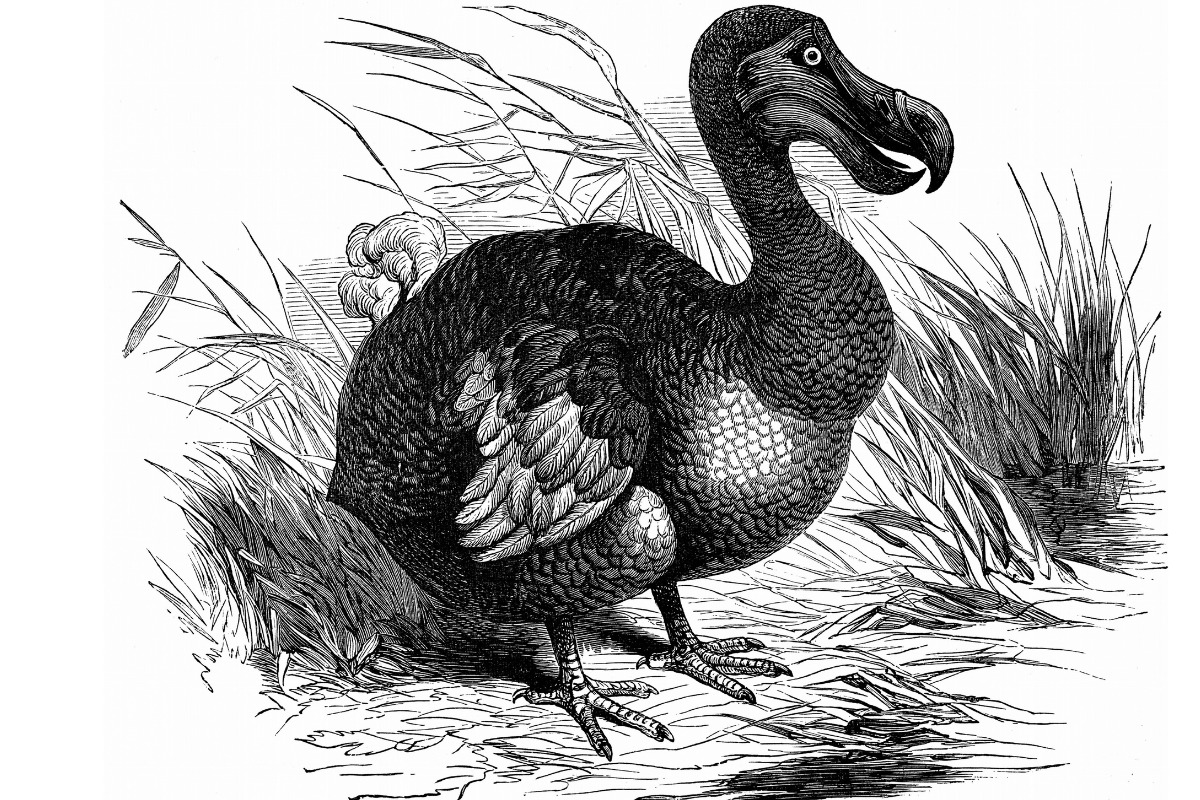

These animals have been on the verge of extinction since 1598 when Dutch sailors were in Mauritius and used them as food during their voyages. However, in reality, it was the advent of other invasive animals that unbalanced the fauna and contributed to the disappearance of the species. Englishman Benjamin Harry’s descriptions of meat spoke of its toughness.
2. Bison Anticus
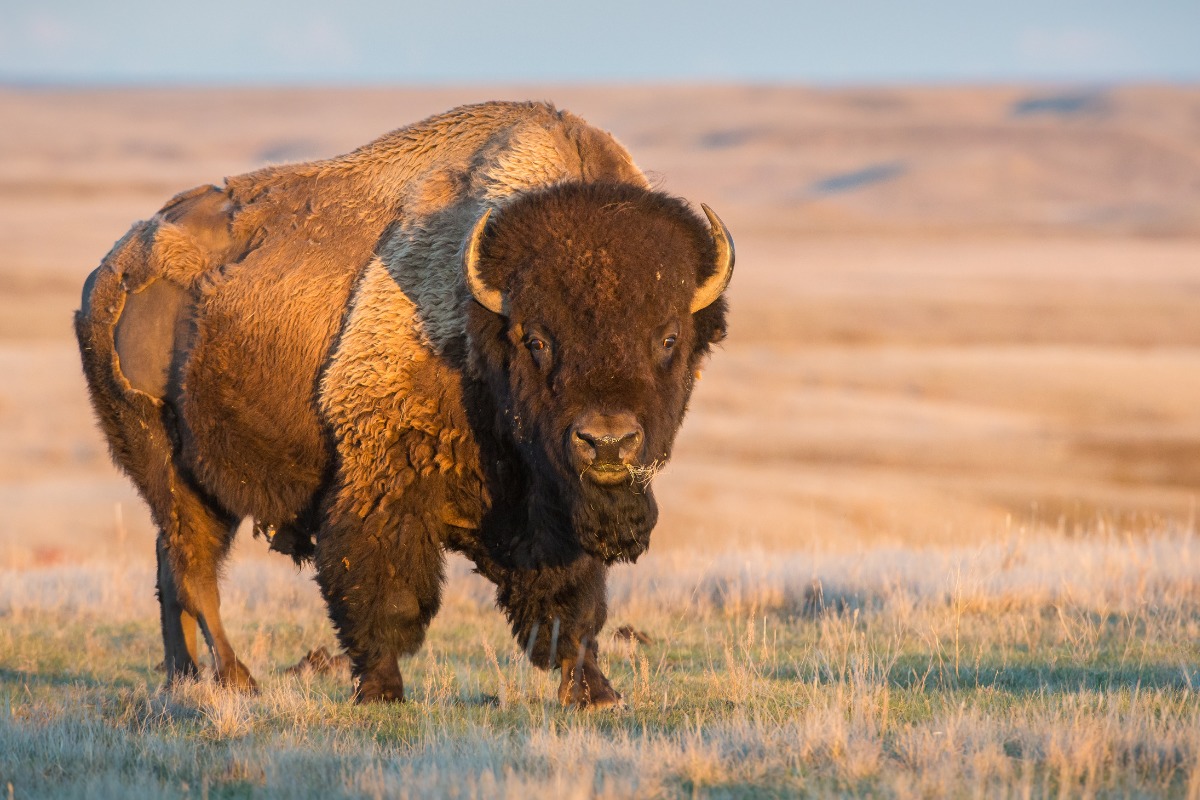

After it was extinct for more than 10,000 years, historians have established its existence through the tools that Native Americans used to slaughter it. In addition to being a source of food, they have also been used as support services.
3. Tailiairon apples
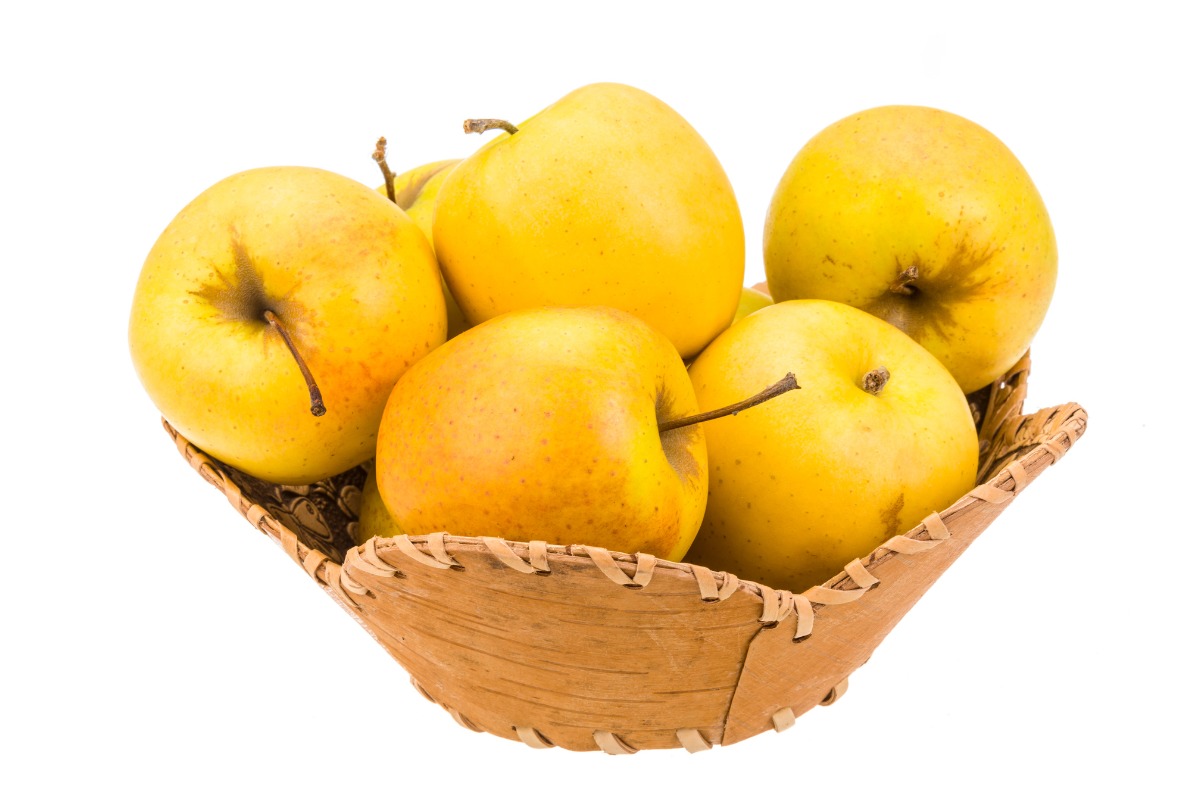

The record of the existence of this fruit is in Thomas Jefferson’s letter to his granddaughter. In the contents of the letter, he explains that the apples he planted in his orchard produced the best quality apples. This letter is dated 1814 and may have lost type with Jefferson’s plantation.
4. Steller’s sea cow
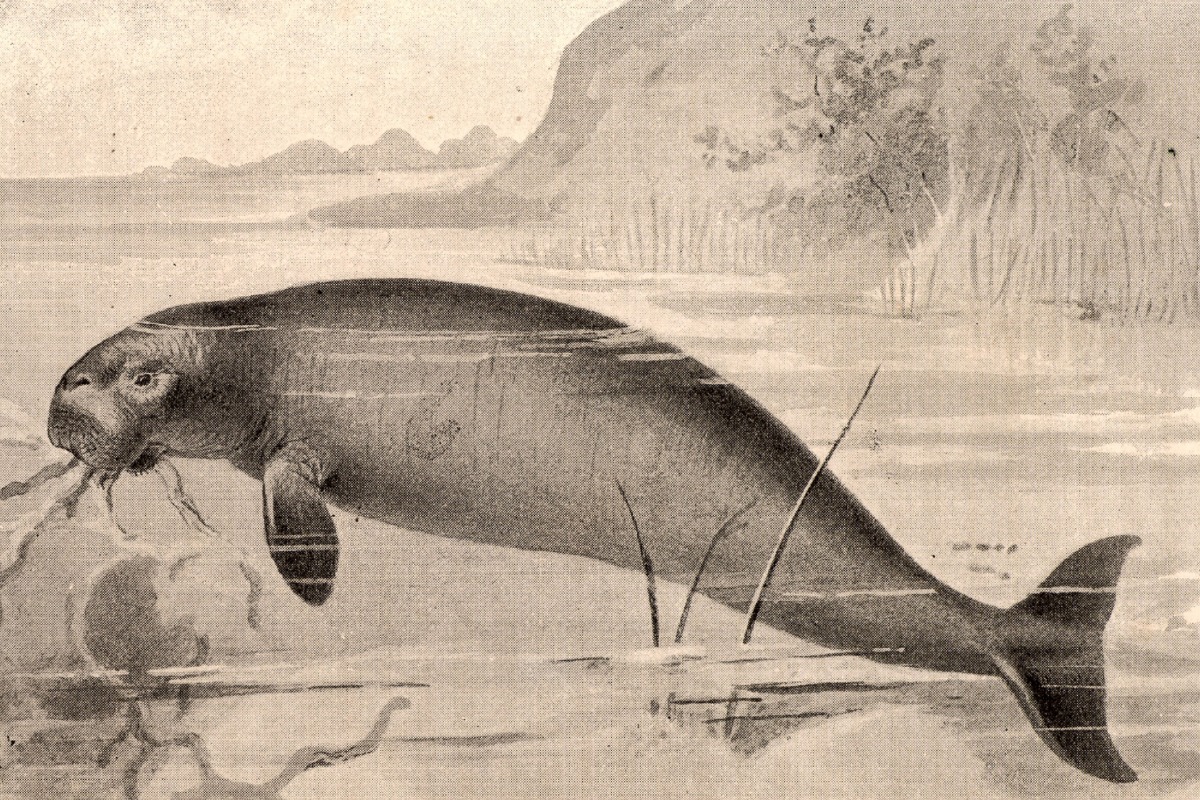
Spotted in the Bering Sea in 1741, this animal had delicious meat. Sailors used its meat and fat. Hunting led to the species’ extinction in 1768, nearly 30 years after its first record.
5. Alka Great

In the 19th century, the species became extinct due to the search for a type of quilt called the quilt. Their meat was also consumed and the first record of the species in fossils is identified as 100,000 years ago, indicating consumption by Neanderthals.



![[VÍDEO] Elton John’s final show in the UK has the crowd moving](https://www.lodivalleynews.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Elton-John-1-690x600.jpg)

More Stories
A South African YouTuber is bitten by a green mamba and dies after spending a month in a coma
A reptile expert dies after a snake bite
Maduro recalls his ambassador to Brazil in a move to disavow him and expand the crisis