During the week, scientists announced important discoveries in astronomy, such as the presence of a fundamental molecule for humans in space and a rare white pulsar. We even had a green meteor of uncertain nature.
Check out these and other news highlights of the week below.
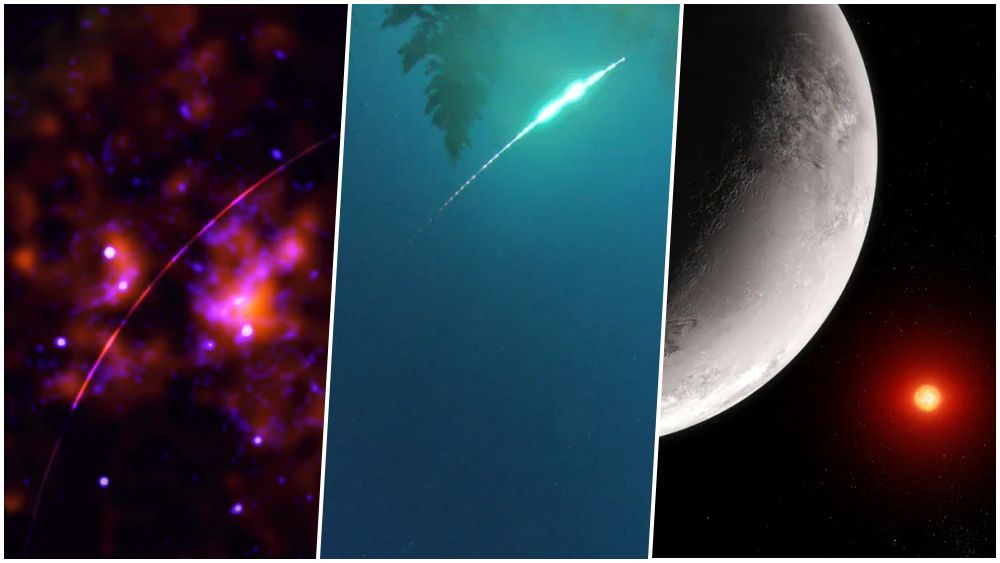
Black hole sound A*
200 years ago, the black hole Sagittarius A*, at the center of the Milky Way, erupted into activity by gobbling up surrounding matter. This interaction caused light to be emitted in different wavelengths, which were reflected from nearby gas clouds.
To describe the phenomenon in other, unseen ways, the researchers flagged the emissions. Radiation is at least a million times greater than current emissions.
Green meteor in the sky of SP and MG
A green meteor was observed in the skies of Sao Paulo, Minas Gerais and Goiás during Monday night (19). It entered the atmosphere at 6:37 pm over Minas Gerais and, after traveling 300 km, ended its journey in São Paulo.
Some astronomers suspect it was a piece of space junk that entered Earth’s atmosphere, but others note that the track is more consistent with a space rock.
The thin atmosphere of the planet TRAPPIST-1 c
The James Webb telescope spotted the planet TRAPPIST-1 c to check its mid-infrared properties, and found that the atmosphere there is composed of carbon dioxide, possibly very thin and cloudy.
This means that the planet must have formed with a small amount of water and compounds necessary for life, but the results are not yet final.
Launching 47 new Starlink satellites
SpaceX launched a Falcon 9 rocket to send new Starlink satellites into space in the early hours of Thursday (22). The huge collection already contains more than 4,600 units. Given the goal of posting 30k, this is just the beginning.
The first stage of the reusable rocket returned to Earth and landed on the Of Course I Still Love You ship in the Pacific Ocean.
The basic molecule for humans is in space
Tryptophan is one of the 20 essential amino acids for the growth of the human body and now it joins the list of those already in the space of its class. It was discovered in a star-forming region called IC348, located in the Perseus molecular cloud.
The discovery indicates that the molecule is common in places where stars and planets form, and of course offers more hope in the search for alien life.
A pulsar that rotates 300 times faster than Earth
A white pulsar has been found spinning 300 times faster than our planet. With each episode, powerful beams of light are shot at a neighboring star, a red dwarf, causing the system to brighten and dim.
In addition to being a very rare type of object, its discovery may confirm some hypotheses of stellar evolution, such as the presence of dynamos in the cores of white dwarfs. This would explain the behavior of the new object, driven by strong magnetic fields.
Craters and volcanic formations on Mercury
During the third flyby of Mercury, the BepiColombo probe approached the planet’s surface and took pictures of the crater, tectonic and volcanic formations.
Only 236 km away, the probe recorded a crater 218 km in diameter, named Manley in honor of Jamaican artist Edna Manley. Astronomers are curious because the crater has a low reflectivity and could reveal remnants of Mercury’s ancient crust.

“Incurable thinker. Food aficionado. Subtly charming alcohol scholar. Pop culture advocate.”





More Stories
NASA Releases Selfie of Perseverance Rover Working on Mars
NVIDIA driver includes hidden Final Fantasy XVI profile
PlayStation Plus Extra and Premium saw a significant drop in players in July