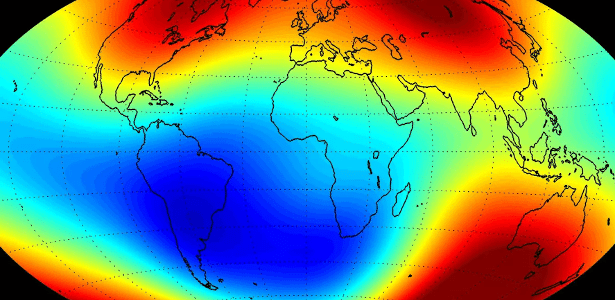
In an interview with tiltHe explains that this anomaly arises due to the difference in density in specific areas of the outer core, which creates an electric current that in turn produces the Earth’s magnetic field. These regions of varying intensity are responsible for the formation of AMAS, which differ from other regions in the Earth’s magnetic field. Heterogeneity in the planet’s core is a critical factor in this configuration. Therefore, AMAS is a complex and unique phenomenon compared to other magnetic regions on Earth.
AMAS is closely associated with the Van Allen Belt, a region of space around Earth where charged particles, such as electrons and protons, are trapped by Earth’s magnetic field. The Van Allen belt consists of two main regions: the inner belt, which is closer to Earth and rich in protons, and the outer belt, which is mainly composed of electrons.
In the AMAS region, the inner belt approaches the planet’s surface, leading to a greater concentration of charged particles in this region. This proximity increases radiation, which could damage satellites and affect the propagation of radio waves, requiring space agencies to take precautionary measures to protect their equipment when passing through this area.
Satellites and radio waves
AMAS can cause damage to satellites and affect the propagation of radio waves due to its interaction with the Van Allen belts. “Space agencies are aware of this problem and try to prevent their satellites from passing through the AMAS region as much as possible,” comments Oliveira.
The proximity of the anomaly to the belts increases the occurrence of charged particles that can damage the electronic components of satellites. To mitigate this risk, space agencies prevent their satellites from passing through the central AMAS region. When necessary, satellites are placed comment (Standby mode) to protect your systems.

“Incurable thinker. Food aficionado. Subtly charming alcohol scholar. Pop culture advocate.”




More Stories
NASA Releases Selfie of Perseverance Rover Working on Mars
NVIDIA driver includes hidden Final Fantasy XVI profile
PlayStation Plus Extra and Premium saw a significant drop in players in July