NASA's PACE satellite has been launched and will monitor Earth's atmosphere and climate. Thus, it will help scientists analyze the state of the oceans
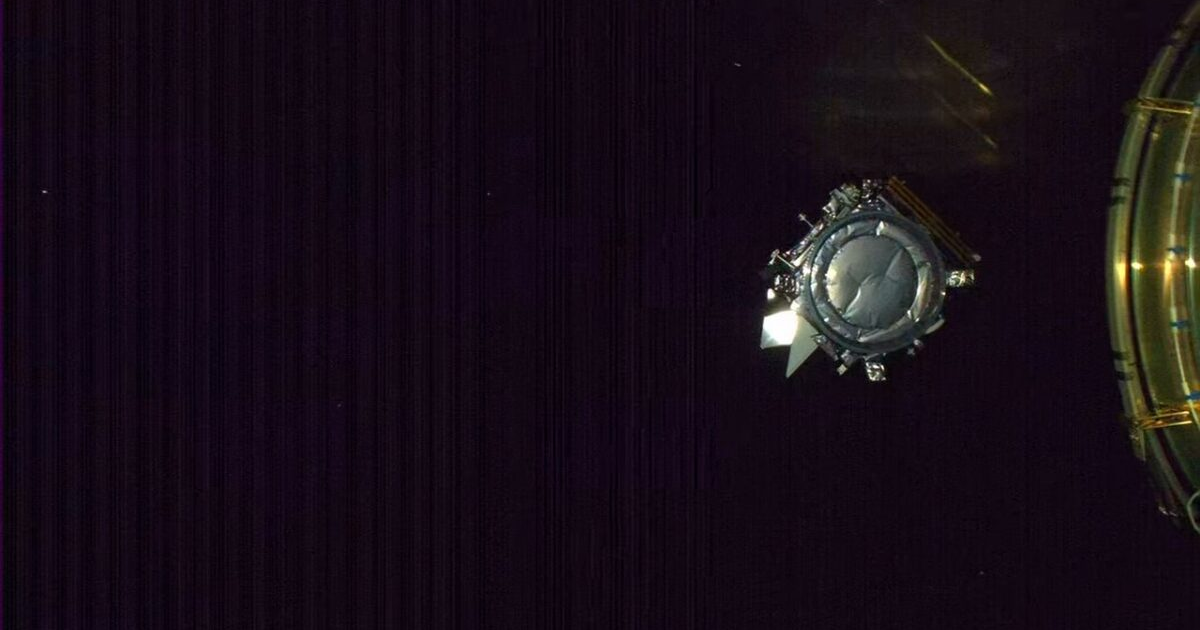
Another satellite from NASA in the space. The satellite, called PACE (short for “Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, Ocean Ecosystem”), was launched during the early hours of Thursday (8) by a Falcon 9 rocket, from… SpaceX. When operations begin, PACE will monitor Earth's atmosphere and climate, which also helps scientists analyze the state of the oceans.
The Falcon 9 rocket departed Space Launch Complex 40 at Space Force Station in Cape Canaveral, Florida, at 3:33 a.m. Brasilia time. About five minutes after launch, the PACE rocket's upper stage fired in an instant Heliosynchronous orbit 677 km above Earth.
We have a take off 🚀
Our PACE spacecraft is on its way to study microscopic organisms in our ocean and molecules in the air. pic.twitter.com/SvxY1EErdx
– NASA (@NASA) February 8, 2024
Now, the PACE components will operate their various subsystems. Next, the mission team will evaluate whether everything is going as expected, and if so, the satellite will be able to begin its science work. According to NASA, ground stations have already contacted PACE and provided preliminary data on its status after launch.
When it comes down to business, the data obtained by the satellite will help scientists understand how carbon dioxide exchanges between the ocean and atmosphere occur, and also reveal how aerosols can affect the growth of phytoplankton. What's more, the data will expand NASA's long-term observations, probing our planet's “vital signs” for decades to come.
To achieve this, PACE has three tools. One is the Ocean Color Spectroradiometer (OCI), which will map the wavelengths of colors determined by interactions between sunlight and molecules in the water. The other devices are polarimeters, which will measure how light's polarization (its in-plane oscillation) is affected by its passage through the ocean, clouds, and land. Atmospheric dust.
source: NASA
Popular on Canaltech:

“Incurable thinker. Food aficionado. Subtly charming alcohol scholar. Pop culture advocate.”





More Stories
NASA Releases Selfie of Perseverance Rover Working on Mars
NVIDIA driver includes hidden Final Fantasy XVI profile
PlayStation Plus Extra and Premium saw a significant drop in players in July