On Saturday (4), in its red list, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) warned that 28% of 138,374 species Already classified in the world as endangered, the equivalent of 38,543 species.
In short, according to the publication, they are endangered:
- 41% of amphibian species;
- 33% of coral reefs;
- 34% are conifers, mostly tree species;
- 26% of mammalian species;
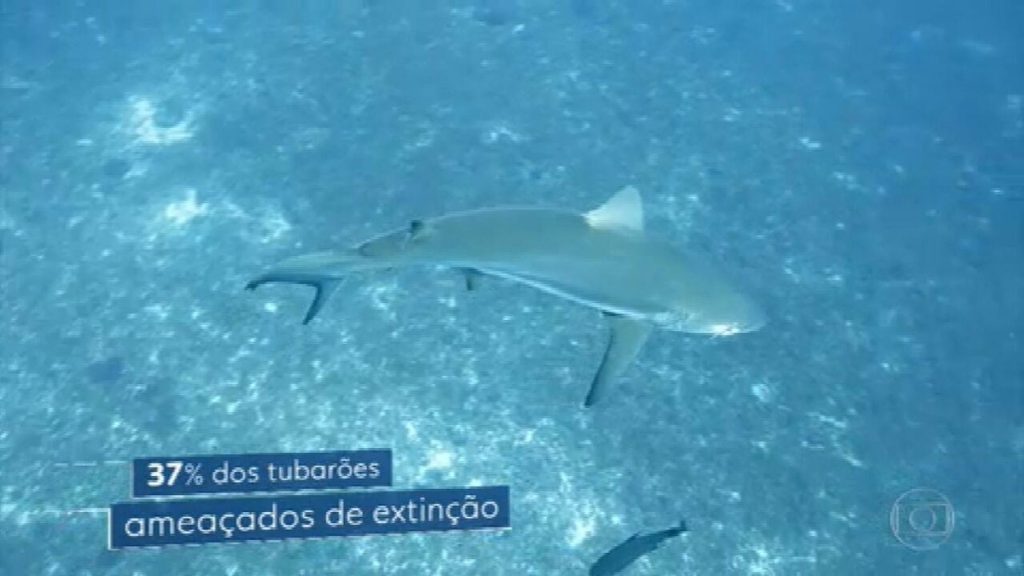
- 37% of species of sharks and rays
- 14% of bird species
One of the highlights of komodo dragonThe largest living lizard in the world is a World Heritage Site. The lizard’s classification has shifted from “vulnerable” to “threatened.” This species is endemic to Indonesia and is only found in Komodo National Park. Due to climate change, sea level rise is expected to reduce the suitable Komodo dragon habitat by at least 30% over the next 45 years.
Andrey-Gudkov recorded fights with a Komodo dragon in Komodo National Park, Indonesia. Photo: Andrei Gudkov/Wild Photographer of the Year
The red list also highlights a file marine species, warning that 37% sharks and rays The world’s cataloged is endangered. In addition, poaching threatens almost Two out of five sharks are extinct. Climate change is also referred to as an exacerbation of the loss and degradation of marine habitats.
On the other hand, the document re-evaluated seven commercially caught tuna species and concluded that four showed signs of recovery thanks to countries implementing more sustainable fishing quotas and successfully combating illegal fishing. One is yellowfin tuna, which has gone from ‘threatened’ to ‘less of concern’.
“Today’s update of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List is a strong sign that despite the increasing pressures on our oceans, species can recover if countries truly commit to sustainable practices,” said Bruno Oberle, IUCN Director-General.
Dozens of endangered rays were found dead on Santos Beach
Among the tuna species that failed to recover is the southern bluefin tuna, which has gone from “endangered” to “threatened.”
The raya viola, an endangered species, was found in the hold of a Brazilian ship this year. – Photo: Disclosure / Environmental Police
30% of trees are threatened
The State of the World’s Trees report, published in August, found that At least 30% of the 60,000 known tree species are at risk of extinction. The alert concerns a total of 17,500 tree species, twice the total number of threatened mammals, birds, amphibians and reptiles, and is also based on IUCN data.
Brazil is cited in the document as the country “which has some of the most biologically diverse forests in the world, has the highest number of tree species (8847) and also the most endangered species (1788).”
Jequitibá an endangered tree, captured in Vassununga State Park – Photo: Tiago Lima / Olhos da Mata Atlântica
The survey also warned that about 142 species have already disappeared from the wild and 442 are on the verge of extinction – in these cases, fewer than 50 individual trees of each species remain.
The critically endangered tree species, according to the study, range from the well-known oak and magnolia trees to the tropical hardwoods found in the Amazon rainforest.
Amazon: Fires have already affected 95% of species
An image shows an anteater dead after a fire in the Amazon near Mirante do Norte, Rondônia, on August 20. Photo: Osley Marcelino/Reuters
A study published on September 1 in the scientific journal “Nature”, with the participation of Brazilian scientists, revealed that the fires that have hit the Amazon region since 2001 may have affected the 95.5% of species of plants and vertebrates are already classified throughout the biome. The scientists used data from the IUCN.
According to the publication by Nature, the human-caused Amazon fire in the past 20 years has already affected the habitat of 85.2% of endangered species of plants and animals, representing 53 of the 55 endangered species of mammals. extinction; 5 of 9 species of reptiles are endangered; 95 out of 107 species of amphibians are threatened with extinction; And 236 of the 264 plant species are threatened with extinction.
Among the endangered mammals directly affected by the fires in the Amazon, the study presents for example some species of spider monkeys and spider monkeys, as well as some examples of birds, such as the Morrissey.

“Music fanatic. Professional problem solver. Reader. Award-winning tv ninja.”





More Stories
Couple retakes glacier photo after 15 years, surprised by changes: ‘It made me cry’
Two killed in hotel collapse in Germany – DW – 07/08/2024
Lula speaks for half an hour on phone with Biden about Venezuela’s electoral impasse | Politics