Conducted a survey An international team of researchers has detailed the precise fossil evidence Which suggests that complex eukaryotic life arrived on Earth earlier than previously thought.
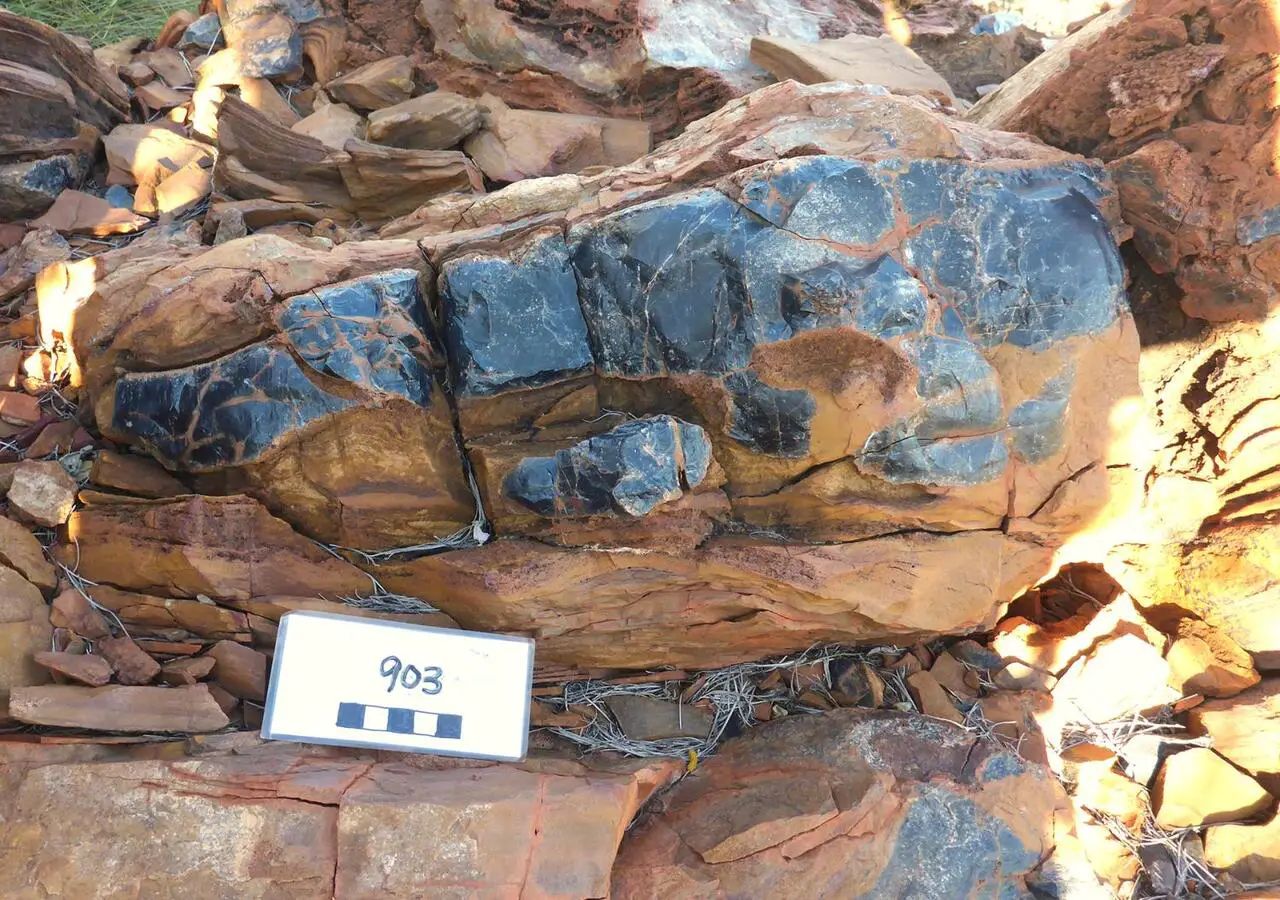
Erica Barlow, Affiliate Research Professor in the Department of Geosciences at Pennsylvania State University, He discovered microfossils in a type of sedimentary rock called black chert. Investigation of this ancient snapshot of Earth’s history has led to new questions surrounding the evolution of life on Earth. The researchers published their findings in the journal Geology.
The great oxidation event
Great Oxidation Event (GOE) It occurred about 2.4 million years ago, with oxygen levels increased significantly through the emergence and spread of cyanobacteria. These bacteria produce oxygen as a byproduct through a vital process called photosynthesis.
The accumulation of oxygen in the atmosphere has changed the Earth’s geology and its biological inhabitants. It causes oxidation of metals on the Earth’s surfaceWhich led to the production of new minerals and the accumulation of iron oxides. ShOne of the Egyptian government’s geological indicators is the widespread occurrence of iron “rust”..
Although the increase in atmospheric oxygen benefited aerobic (oxygen-dependent) organisms, it was likely devastating to many anaerobic (non-oxygen-dependent) life forms that previously dominated the Earth. This event determined the course of the Earth’s biosphereThe preference of organisms adapted to live in a high-oxygen environment.
Life on Earth
The general consensus among the scientific community is that prokaryotic life forms – archaea and bacteria, for example – They arose before more complex eukaryotic life forms.
Compared to modern organisms, #Pennsylvania state Researchers with @GeoscPSU Microfossils say they resemble a type of algae more than prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria, for example, that existed before the Great Oxidation Event: https://t.co/CukMf1h3xc pic.twitter.com/6XC7WhWUAP
— Penn State Research (@PSResearch) November 14, 2023
Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells contain what is called a true nucleus, a region containing linearly organized DNA surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Eukaryotes (such as fungi, plants, algae, and animals) also contain membrane-bound organelles, which are subcellular structures responsible for carrying out essential tasks to support proper cellular function.
“Big claim”
The researchers investigated the microfossils, noting that they were actually larger than other microfossils that existed before the GOE event. The team also noted Their overall shape is spherical, something we have not yet seen in the fossil record.
“I think finding a relatively large and complex fossil, relatively early in the history of life on Earth, makes us wonder: “If we find life elsewhere, it may not just be prokaryotic bacterial life.”The teacher said. Barlow. “Maybe there’s a chance there’s something more complex preserved – Even if it’s still microscopic, it could be something from a slightly higher level.
Barlow explains The microfossils are similar to modern green algae in the family Volvocaceae. “This suggests that the fossil may be an early eukaryotic fossil. This is a big claim and needs more work, but it raises an interesting question that the community can develop and test.”
More research is needed to determine whether microfossils were left by eukaryotic speciesBut the idea has important consequences, according to experts. As a result, the known record of eukaryotic microfossils will advance by 750 million years.

“Incurable thinker. Food aficionado. Subtly charming alcohol scholar. Pop culture advocate.”






More Stories
NASA Releases Selfie of Perseverance Rover Working on Mars
NVIDIA driver includes hidden Final Fantasy XVI profile
PlayStation Plus Extra and Premium saw a significant drop in players in July