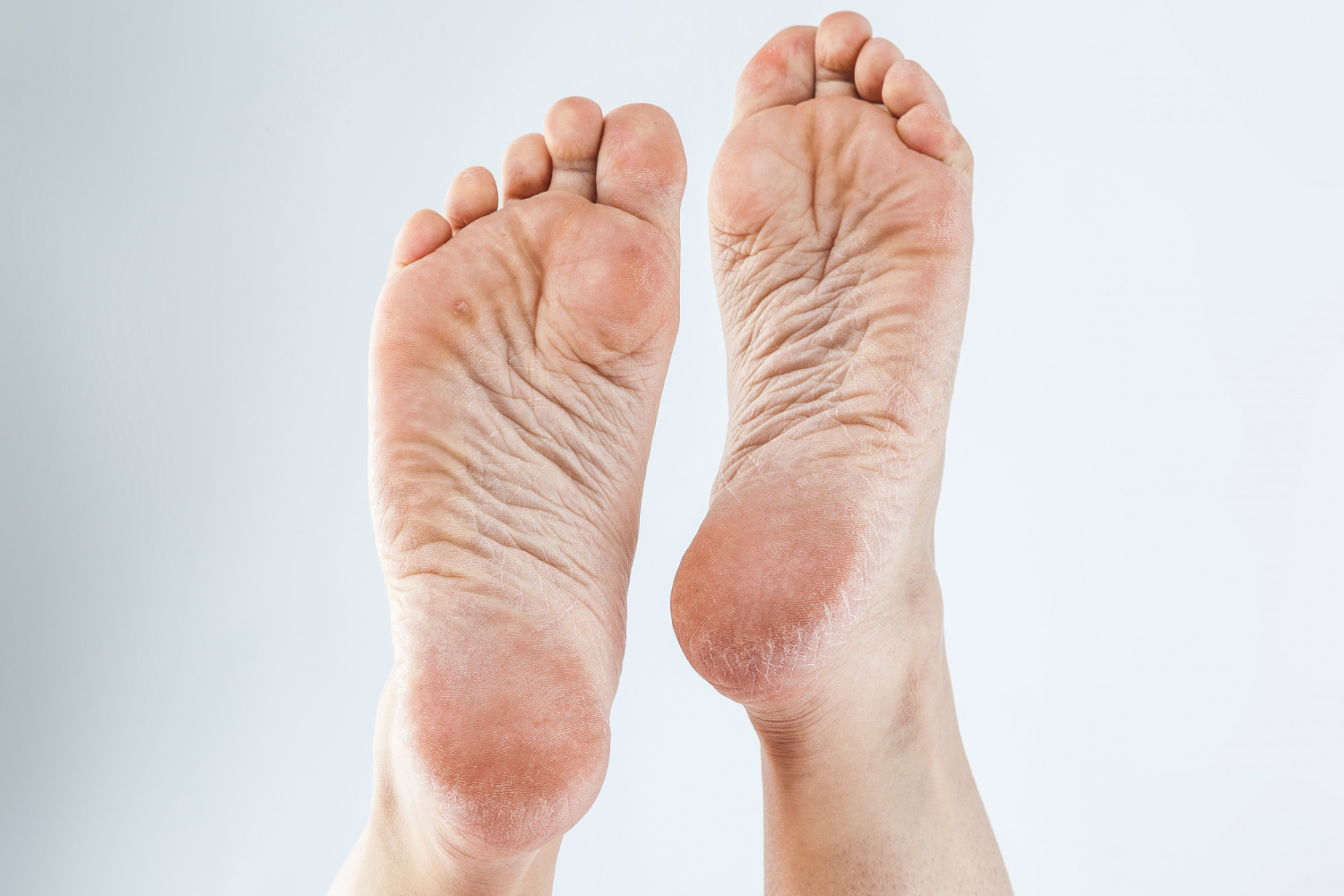
Believe it or not, some people end up neglecting their feet when it comes to personal hygiene. When taking this relaxing shower, you should never forget to wash your extremities. Although scrubbing your feet takes a bit more work, it is essential to create a habit. Learn about the risks associated with not cleaning properly to prevent various problems, such as infections and allergies.
See also: Do you drink? A tech company brews beer made from bathwater
Don’t you want to wash your feet every day? See what can happen
1. Smelly feet
Poor foot hygiene allows sweat and bacteria to build up, creating a favorable environment for the development of unpleasant odors. In this case, sweating produces an unpleasant odor that leads to embarrassment.
This especially happens with those who spend the whole day outside, wearing tight shoes. Try anti-fungal talc and when you get to your house, remove your shoes and run to the bathroom immediately.
2. The presence of bacteria and fungi
In addition, not washing frequently promotes the spread of fungi, such as tinea pedis or ringworm. These fungal infections can cause itching, scaling, redness, and even blisters between your toes.
Without proper treatment, this condition often spreads to other areas, causing constant discomfort. In this way, the feet do not allow moisture to accumulate. Wash them with plenty of soap and warm or cold water.
3. The appearance of cracks and even injuries
Another negative consequence of not washing your feet daily is cracked skin. Therefore, the accumulation of dirt and dead cells causes dryness and cracks in the heels and other parts of the skin.
In more serious cases, a lack of proper foot hygiene can lead to injuries, such as open wounds or sores. This is particularly worrisome for people with diabetes or circulatory problems. Therefore, the most severe cases include severe infections and even amputation in patients with comorbidities.

“Hardcore beer fanatic. Falls down a lot. Professional coffee fan. Music ninja.”




More Stories
The law allows children and adolescents to visit parents in the hospital.
Scientists pave the way for the emergence of a new element in the periodic table | World and Science
Can dengue cause hair loss? Expert explains how the disease affects hair